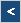
| Concurrent Statement | ---- used in ----> | Architecture |
| Syntax |
signal_name <= expression_1 when condition_1 else
expression_2 when condition_2 else
expression_3 ;
|
| Rules and Examples |
Each condition is aboolean expression:
architecture COND of BRANCH is
begin
Z <= A when X > 5 else
B when X < 5 else
C;
end COND; |
Conditions may overlap, as for the if
statement. The expression corresponding to the first "true" condition is
assigned.
architecture COND of BRANCH is
begin
Z <= A when X = 5 else
B when X < 10 else
C;
end COND; |
There must be a final unconditional else expression:
architecture COND of WRONG is begin Z <= A when X > 5; --illegal end COND; |
| The expressions assigned may be delayed. Transport delay mode may also be specified |
Conditional signal assigments may be used to define tri-state
buffers, using the std_logic and std_logic_vector
type. Note the use of the aggregate form for
a vector bus.
architecture COND of TRI_STATE is
signal TRI_BIT: std_logic;
signal TRI_BUS:
std_logic_vector(0 to 7);
begin
TRI_BIT <= BIT_1 when EN_1 = '1'
else 'Z';
TRI_BUS <= BUS_1 when EN_2 = '1'
else (others => 'Z');
end COND; |
| Synthesis Issues |
A conditional signal assignment will usually result in combinational logic being generated. Assignment to 'Z' will normally generate tri-state drivers. Assinment to 'X' may not be supported.
If a signal is conditionally assigned to itself, latches may be inferred.
| Whats New in '93 |
In VHDL-93, any signal assigment statement may have an optinal label.
VHDL-93 defines an unaffected keyword, which indicates a condition when a signal is not given a new assignment:
label: signal <= expression_1 when condition_1
else expression_2 when condition_2
else unaffected ;
The keywords inertial and reject may also be
used in a conditional signal assignment.
A conditional signal assignment can be specified to run as a postponed process.