Configuration Declaration
Formal Definition
A configuration is a construct
that defines how component instances in a given block are bound to
design entities in order to describe how design entities are put
together to form a complete design.
Simplified Syntax
configuration
configuration_name of entity_name is
-- configuration declarations
for architecture_name
for instance_label:component_name
use
entity library_name.entity_name(arch_name);
end
for;
-- other for clauses
end for;
end [configuration]
[configuration_name];
configuration
configuration_name of entity_name is
-- configuration declarations
for architecture_name
for instance_label:component_name
use
configuration library_name.config_name;
end
for;
-- other for clauses
end for;
end [configuration]
[configuration_name];
Description
Each component instantiation refers to some design entity
(entity/architecture pair) and the association is specified by a configuration
specification. Component specification appears in the
declarative part of the unit, where the instances are used. If for
some reasons, however, it is appropriate (or desired) to postpone (or
defer) such association until later, configuration
declaration can be used for specifying such deferred
component specifications.
The configuration declaration starts with the configuration name and
then it is associated to a given design entity. Declarative part of
the configuration may contain use clauses,
attribute specifications
and group declarations. The
main part of the configuration declaration contains so called block
configuration. It indicates which architecture will be used
with the entity specified earlier, as well as which configuration
elements will be used in the component instantiation. This
declaration may contain other blocks' configurations, allowing this
way to specify hierarchical structures. Such a configuration can be
called hierarchical, while
a configuration without hierarchy can be called simple.
A simple configuration contains reference to only one architecture
body (Example 1).
Hierarchical configurations, on the other hand, allow to nest block
configurations (Example 2). This mechanism allows binding component
instantiation statements with the design entities down the hierarchy.
When the ports and generics in component declaration do not match
with their counterparts in entity declaration, so called binding
indication can be applied. Simply speaking this is an
explicit notification on how the ports and generics in the entity
should be bound to ports and generics of the component instance. The generic
map and port map
clauses are used for this purpose. This technique is used in Example
1. In practice, however, it is recommended to match the generics and
ports of components and respective entities as this improves readability.
Two main binding methods that can be applied in configuration
specifications: binding of entities and binding configurations. They
are illustrated in Examples 1 and 3, respectively.
Examples
Example 1
entity INVERTER is
generic
(PropTime : TIME := 5 ns);
port ( IN1 : in
BIT; OUT1 : out BIT);
end INVERTER;
architecture STRUCT_I of
INVERTER is
begin
OUT1 <= not
IN1 after PropTime;
end STRUCT_I;
entity TEST_INV is end TEST_INV;
architecture STRUCT_T of
TEST_INV is
signal S1, S2 : BIT := '1';
-- INV_COMP component declaration:
component INV_COMP is
generic (TimeH : TIME);
port ( IN_A : in
BIT; OUT_A : out BIT );
end component;
begin
-- instantiation
of INV_COMP component:
LH:INV_COMP generic map
(10 ns) port map (S1,S2);
end STRUCT_T;
configuration CONFIG_TINV of
TEST_INV is
for STRUCT_T -- indicates
architecture body of TEST_INV
-- indicates design entity for LH instantiation statement:
for LH : INV_COMP
use entity
WORK.INVERTER (STRUCT_I)
-- indicates generic and port aspects:
generic map
(PropTime => TimeH)
port map
(IN1 => IN_A, OUT1 => OUT_A);
end for;
end for ;
end CONFIG_TINV;
The CONFIG_TINV configuration declaration can be used as an example
of the basic configuration declaration. There is only one block
configuration in the configuration declaration. This block contains a
component declaration INV_COMP. In the component instantiation
statement LH, the design entity INVERTER is assigned to INV_COMP component.
There is one block configuration in the CONFIG_TINV configuration
declaration, it indicates that STRUCT_T architecture body will be
used. INV_COMP component configuration appears in the block
configuration. The CONFIG_TINV configuration for the TEST_INV design
entity allows associating LG component: INV_COMP with INVERTER design
entity and its STRUCT_1 architecture body.
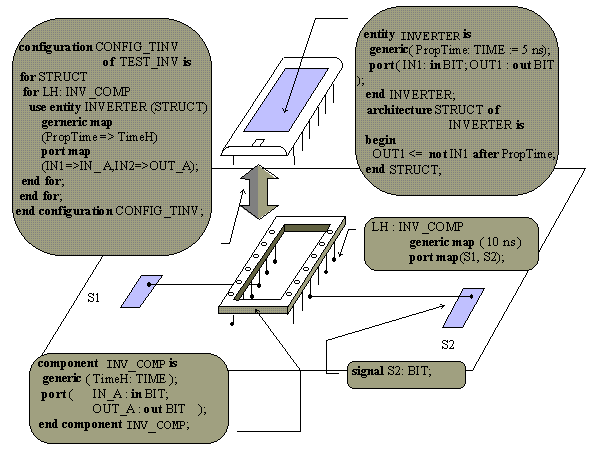
Figure 1. Example of configuration declaration
Example 2
-- block configuration for architecture body STRUCT:
for STRUCT
-- component configuration specified in architecture body STRUCT:
for SPEECH_CPU: SPEECH
use entity SP_LIB.DIG_REC(ISD)
generic map
(TimeRec => 20 sec);
-- block configuration for
architecture body ISD of DIG_REC:
for ISD
-- component configuration
specified in architecture body ISD:
for
AD_CONV : ADC_1 -- relates to instance AD_CONV of ADC_1
use entity ANALOG_DEV.ADC;
end for;
-- for AD_CONV
end for;
-- for ISD
end for;
-- for SPEECH_CPU
end for;
-- for STRUCT
The block configuration, indicating architecture body STRUCT, appears
in the configuration declaration. Next, in the block configuration
there is the component configuration SPEECH, which also contains
block configuration IST. The block configuration IST configures the
architecture body IST which contain an instantiation statement with
label AD_CONV. The entire block is hierarchically specified here.
Example 3
configuration Conf_Test of
Test is
for STRUCTURE_T
for
T_1 : DEC use configuration CONF_E;
end for;
end for;
end configuration Conf_Test;
In this example, the configuration declaration of design entity
EXAMPLE is used. It binds EXAMPLE design entity to DEC component by
using its configuration CONF_E as an entity aspect for T_1 component
instance in the body architecture STRUCTURE_T.
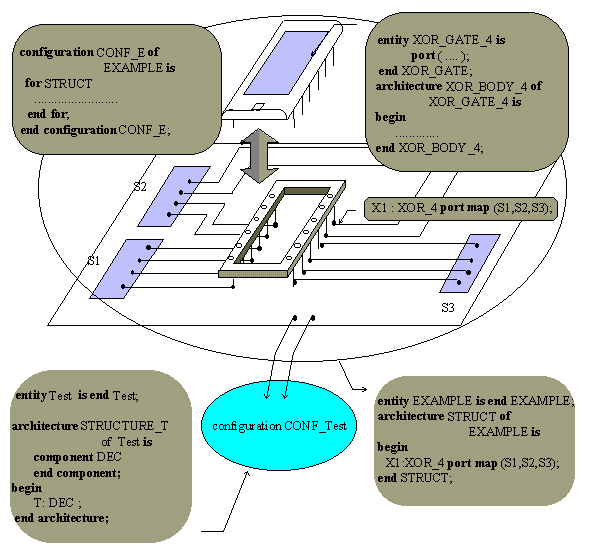
Figure 2. Example of configuration declaration
Important Notes
-
Configuration assigns one and only one architecture to a given entity.
-
Synthesis tools do generally not support configurations.
-
For a configuration of some design entity, both the entity and the
configuration must be declared in the same library.
|